Revolutionizing Startup Marketing: A Comprehensive Analysis of 9 Frameworks for Effective Strategies (Part 1)
Tuesday, 29/11/2022 09:00 (GTM +7)
Given the rising standards of living and increasingly stringent product requirements, startups and marketing professionals require the support and integration of valuable tools to succeed.
This article, ITI Fund will delve into popular and widely-used strategic frameworks for businesses.
1. Marketing Mix (7Ps)
The Marketing Mix is one of the most widely-used traditional marketing frameworks in business. While the original model focused on the 4Ps of Product, Price, Place, and Promotion, with less emphasis on customer service, Booms and Pitner have since added three additional “P” service combinations: People, Process, and Physical Evidence, to aid in brand development.

The 7Ps model provides startups with a comprehensive framework to analyze and optimize every aspect of their company and strategy, enhancing their overall business performance.
- Product: How do startups develop products or services?
- Price: How do startups change their pricing model?
- Place: What novel distribution channels are available for customers to interact with the product (online, in-store, mobile)?
- Promotion: How to add or combine paid, owned and monetized media channels?
- Process: What internal process barriers affect delivering the best value to customers?
- People: Could you provide information about your workforce, and is there a need for skills improvement among your employees?
- Physical Evidence: How to enhance the customer experience (impressive architectural design, well-trained personnel, and a user-friendly website)?
2. STP Marketing
STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning) assists startups in researching and selecting the appropriate market segment to concentrate on exploiting. The essence of STP is to focus on a specific group of target customers rather than expanding to multiple audiences, utilizing competitive advantages to capture a selected market segment.

Segmentation
This initial stage in developing an STP strategy involves classifying potential target products and dividing the market into segments based on customer characteristics. This process offers several benefits for startups, including:
- Providing a comprehensive view to focus on resource allocation
- Helping businesses understand their competitive advantage and market position
- Offering a unique market perspective compared to competitors
To segment the market effectively, startups must consider the following characteristics:
- Measurability: determining the profitability, demand, and purchasing power of the segment
- Accessibility: the ability to reach and interact with customers in the target segment
- Sustainability: considering the market segment to be profitable and providing sustainable value compared to other segments
- Actionability: the ability to serve customers and have a competitive advantage over competitors in the segment.
Targeting
After segmentation, the startup needs to decide which group will be the target market and ensure the following criteria.
- After segmenting the market, startups must evaluate potential target markets based on size, profitability, growth prospects, and competition. These factors are closely related to the target segment’s growth and must be carefully considered.
- To ensure success in the selected market segment, startups must carefully evaluate their competitors’ advantages. This evaluation will help the startup determine whether it is competitive enough to dominate the market. It also needs to analyze whether that segment is profitable closely and supports the company’s long-term goals.
Positioning
Positioning is a strategic process that involves identifying and developing unique advantages that make a product or service suitable for a specific target market. The goal is to occupy a distinct and valuable position in the customer’s mind. Including
- Brand positioning on product differentiation (quality, price, etc.)
- Brand positioning on product attributes or benefits.
- Brand positioning on customer experience and feelings
- Brand positioning is based on product usage.
- Brand positioning by competitors.
3. Porter’s five forces
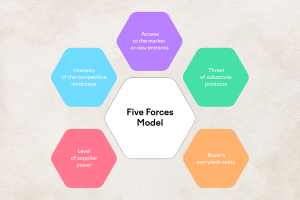
Through researching and understanding the business and operation of many famous brands worldwide, Michael Porter has developed this model to help companies identify each industry’s strengths and weaknesses. In addition, Potter provides appropriate development strategies for the future, including:
Competition in the industry
Competitors are individuals, organizations, and businesses that offer similar products or services to the company, targeting the same customer segment and competing on factors such as price and quality.
- In terms of quantity: if fewer businesses are involved in a product or field, the attractiveness of that product will decrease.
- In terms of capacity: if a product has many competitors but is not too strong, that pressure will have little impact on the business.
The potential of new entrants into the industry
Potential competitors are businesses, individuals and organizations that can participate in the industry:
- Startups need to study the market and business items carefully; they may not have entered the industry right now, but they can not guarantee that they will not participate in the future.
- If the product is competitive and profitable, businesses will deftly enter the industry and occupy a dominant position in the market.
To minimize the rate of competition, startups need to focus on creating barriers to prevent other businesses from entering the industry by:
- Create a different product
- Expand production to reduce costs and product price
- Omnichannel sales
Power of suppliers
Suppliers are organizations and individuals directly involved in the supply of raw materials, goods and services with the following characteristics:
- Suppliers directly determine the selling price of products and the profits of the business.
- Suppliers increase or decrease the cost of output products, causing businesses to struggle when they bear the risk of loss.
- Suppliers may compromise product quality to maintain profits due to high input material costs, which can harm the reputation of enterprises.
- The fewer suppliers in the market, the greater the risk for the business.
Power of customers
Customers are end consumers, agents or retail distributors:
- In a market with numerous goods and enterprises, the availability of more choices for consumers can increase the competitive pressure on businesses.
- The substitutability of products can lead customers to switch from one brand to another if a business fails to maintain consistency in both the quantity and quality of its goods, thereby posing a risk to the business’s customer base.
The threat of substitute products
This needs to be researched and updated continuously because of the novelty and constant change of the market, with the following characteristics:
- Make big pressure on businesses.
- Alternative products were born with new features, beautiful designs and better quality, but the price remained unchanged.
Nowadays, startups must innovate to develop products to earn better profits continuously.
Contact:
itifund.com
(+84)90 998 3699
info@itifund.com
fb.me/ITIFund









